射頻同軸連接器選型與仿真 Rf coaxial connector selection and simulation
什么是射頻同軸連接器?
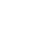
在入門學習微帶貼片天線仿真的時候,我們往往采用簡單的波端口或集總端口進行激勵。但是實物加工測試的時候,就有必要加入一個射頻同軸連接器。其主要作用是為了實現設備/模塊之間的互聯,有效傳遞射頻、微波信號。射頻同軸連接器通常由內導體、外導體、絕緣體以及連接結構等部分組成。
同軸連接器的分類?
常用的射頻同軸連接器的類型有:
SMA(SubMiniature version A)連接器:一種應用廣泛的小型射頻同軸連接器,具有體積小、頻帶寬、性能穩定等特點,一般上限工作頻率為18GHz,現在部分廠商已經可以將SMA最高頻率做到26.5GHz。
SMA界面圖
SMP(SubMiniature Push-On)連接器:一種超小型推入式射頻同軸連接器,SMP連接器的尺寸非常小,有助于實現設備的小型化和高密度集成,適用于空間受限的應用場景。其通常能在較寬的頻率范圍內工作,DC到40GHz,甚至部分型號可更高。
![]()

SMP連接器
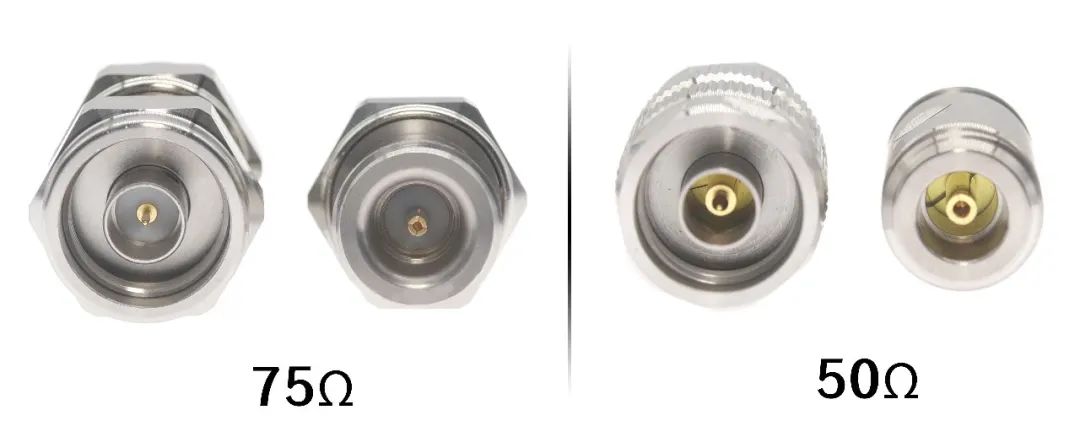
N型連接器:N型連接器是一種常見的射頻連接器,其插頭和插座都具有密封性能,能夠承受高功率、高電壓和高頻率的應用環境。N型連接器采用一種內螺紋設計,可用于在射頻和微波設備和系統中傳輸信號。它是一種通用性高、頻率范圍廣、使用方便、可靠性高的連接器。N型連接器通常有50歐姆和75歐姆兩種規格,其頻段范圍可從0GHZ至11GHz,有些型號甚至能夠達到18GHZ,因此N型連接器被廣泛應用于雷達、天線、衛星通訊、微波測量等領域。N型連接器的優點包括機械強度大、防水防塵性能好、抗老化性能強、性能穩定、易于安裝和拆卸、接觸和信號傳輸性能優良等。此外,N型連接器的缺點是體積較大,不能滿足高密度集成的要求,同時價格也比其它類型的連接器略貴。
![]()

N型連接器
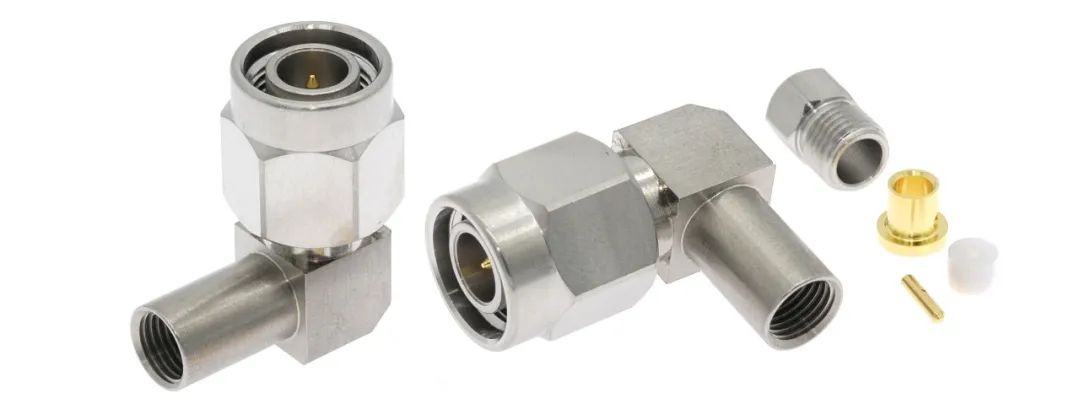
TNC(Threaded Neill–Concelman)連接器:TNC 連接器采用螺紋連接方式,相比一些卡口式連接,連接更為牢固,在振動等環境下也能保持穩定的連接,具有良好的抗震性。例如在一些移動通訊設備中,即使設備經常受到振動,TNC 連接器也能確保信號的穩定傳輸。

TNC連接器
BNC(Bayonet Nut Connector)連接器:常用于視頻監控、儀器儀表等領域。一般支持的信號頻率范圍為 0 到 4GHz,有高精度的 BNC 連接器頻率可達 12GHz 或更高。常見的特性阻抗有 50 歐姆與 75 歐姆兩種,其中 50 歐姆的 BNC 連接器主要用于射頻信號傳輸等大多數射頻應用;75 歐姆的 BNC 連接器則常用于廣播、音頻 / 視頻和低頻通信等結構。

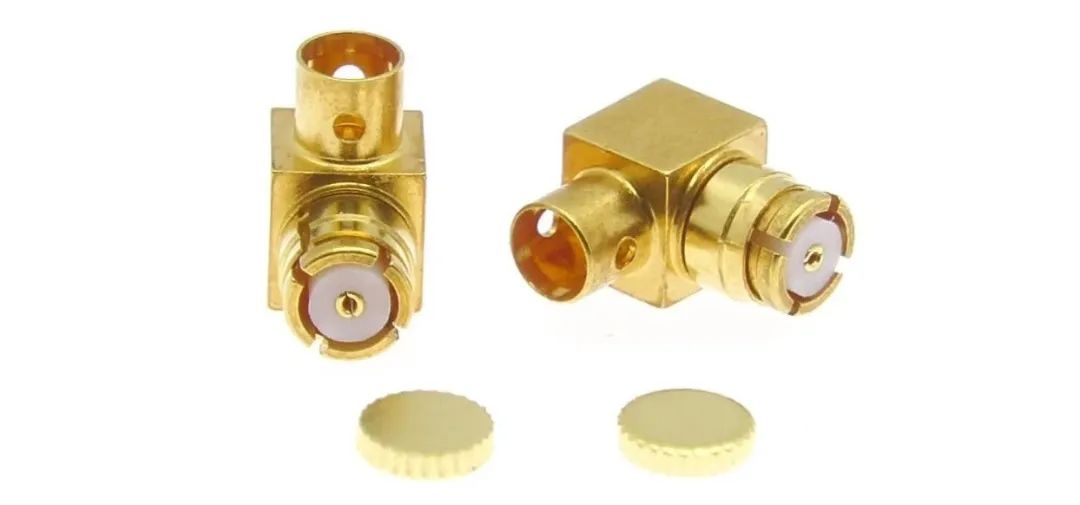
![]() BNC轉接器
BNC轉接器
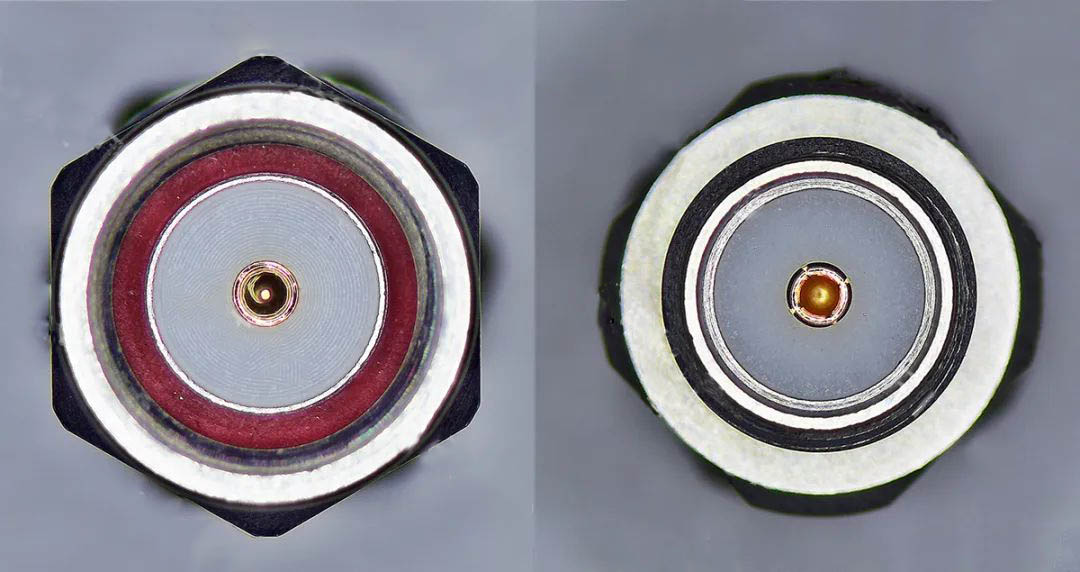
除此之外,在射頻同軸連接器中,有時候還有2.4mm/3.5mm/2.92mm連接器這些代稱。它們通常是指連接器的尺寸規格或接口類型,代表不同的連接器特性和應用場景。
2.4mm 連接器:具有非常高的頻率范圍,可支持到 50GHz 甚至更高。它的尺寸相對較小,具有低反射和低損耗的優點。主要用于極高頻率的射頻系統,如高端測試設備、毫米波通信等領域。 2.92mm 連接器:具有較高的頻率范圍和低損耗特性。它的工作頻率可以高達 40GHz 甚至更高。常用于高頻測試測量設備、微波通信系統、雷達等對頻率要求較高的領域。 3.5mm 連接器:其頻率范圍通常可達到 26.5GHz 左右,最高可達34GHz。相比 2.92mm 連接器,它的尺寸稍大一些。在一些中高頻的射頻應用中較為常見,如通信設備、電子測試儀器等。
如何選擇連接器
對于我們射頻和天線設計而言,常用的射頻連接器集中在SMA和SMP類型。大家根據自己所需的頻段選擇對應的連接器大類。不過,在實際應用中,選好大類后還有進行小類別細分。這里就需要根據實物設計的裝配方式來因地制宜了。
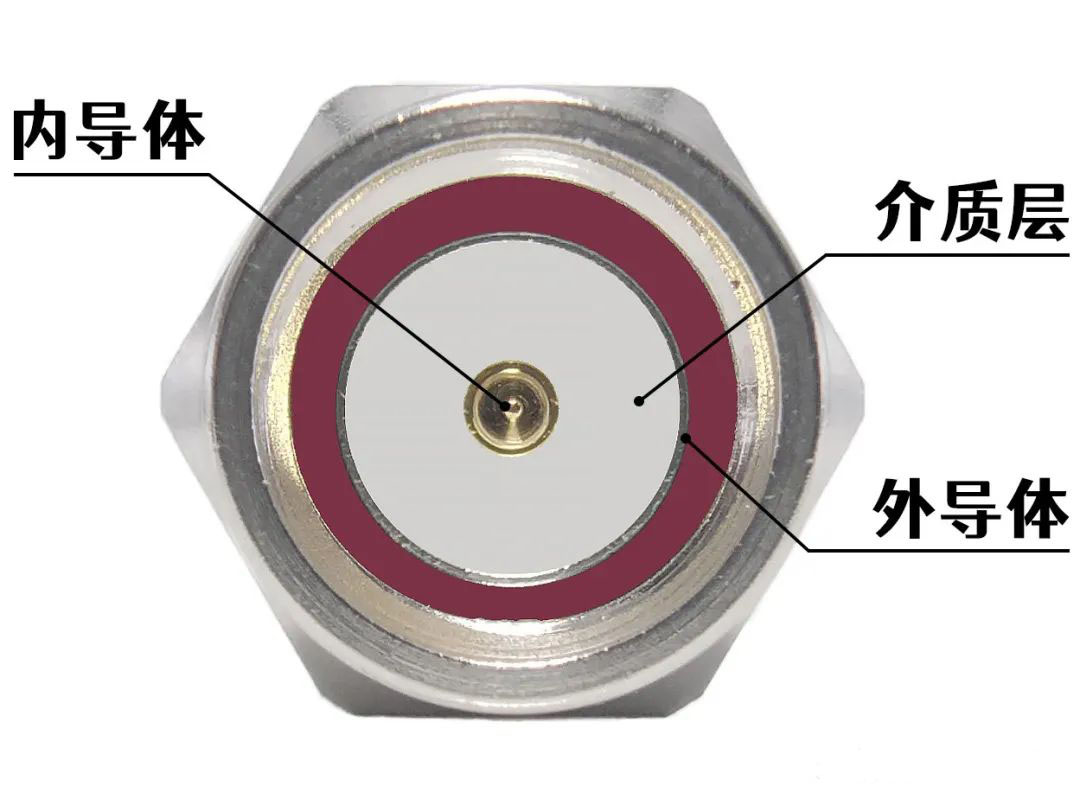
例如,側饋式和背饋式微帶貼片天線就可以分別選擇下圖兩種SMA連接器。
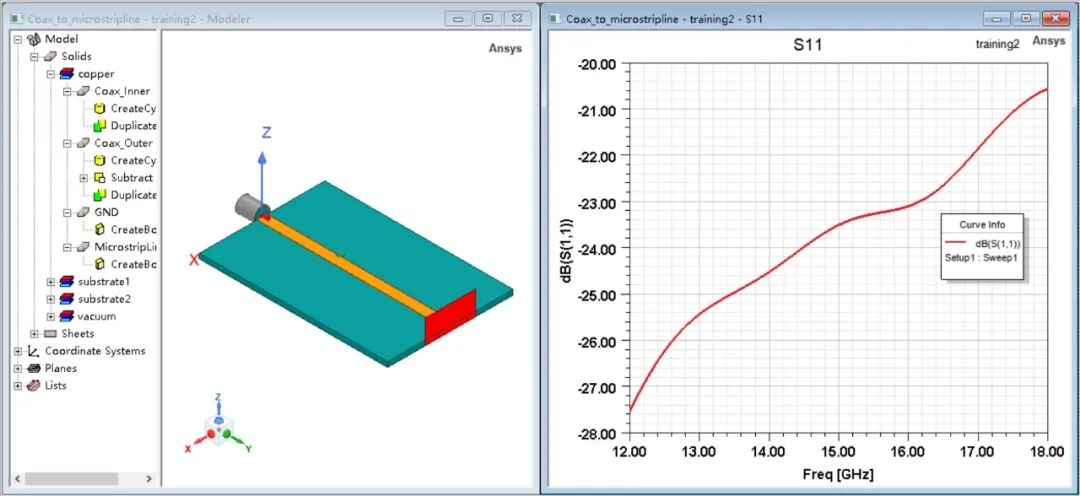
 雖然這些連接器是按50歐姆標準進行設計的,但實際饋電中若不進行電磁仿真,很容易造成端口失配的現象。以50歐姆同軸線和微帶線級聯為例。下圖所示的仿真模型僅考慮理想的同軸線與微帶線級聯,其同軸線的端口反射系數在12~18GHz內均小于-20dB。
雖然這些連接器是按50歐姆標準進行設計的,但實際饋電中若不進行電磁仿真,很容易造成端口失配的現象。以50歐姆同軸線和微帶線級聯為例。下圖所示的仿真模型僅考慮理想的同軸線與微帶線級聯,其同軸線的端口反射系數在12~18GHz內均小于-20dB。
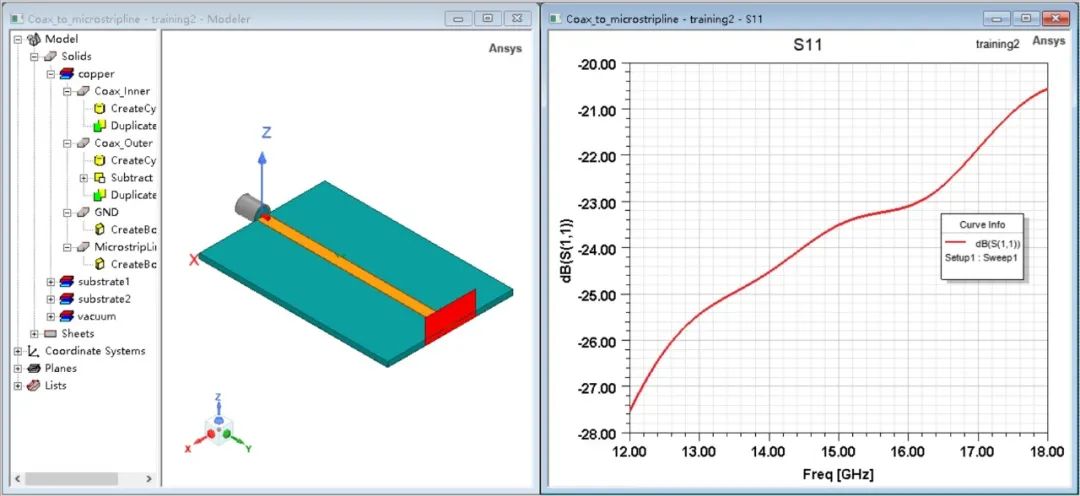
如果仿真完后直接去買來一個射頻同軸連接器焊接上進行測試,我們就會發現端口反射系數在高頻會迅速惡化。這是因為連接器上的法蘭盤多了2條金屬柱,造成了阻抗的不匹配現象。
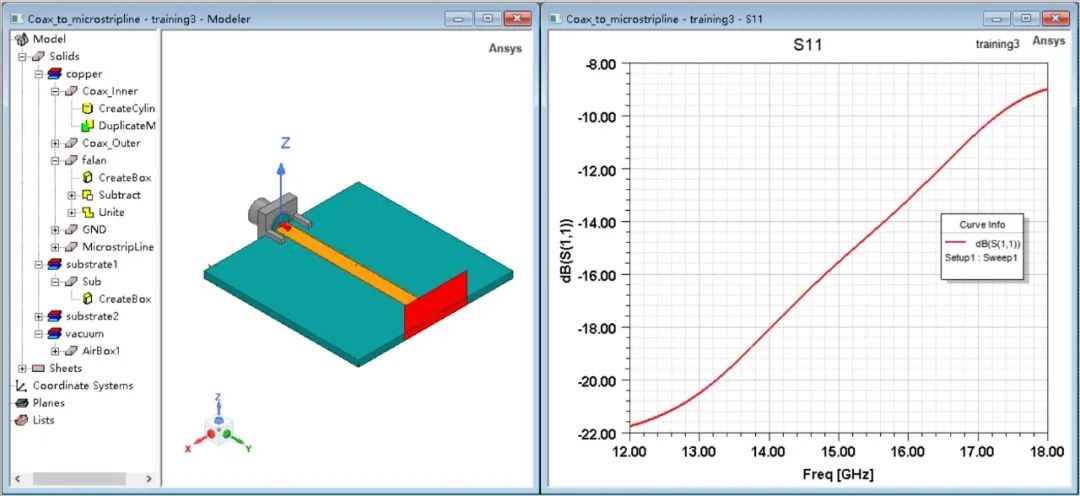
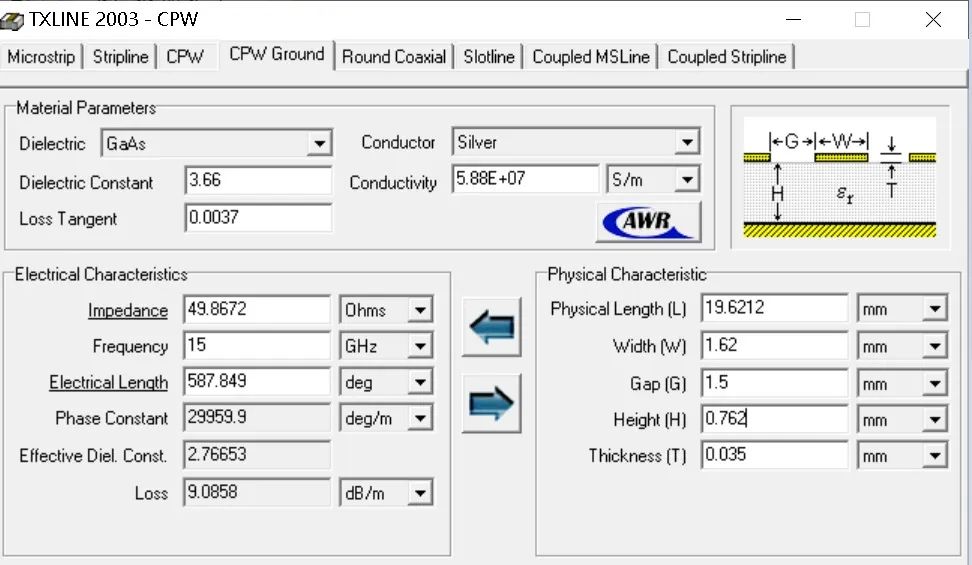
為了優化傳輸系數,我們可以考慮在金屬柱下方增加2條接地的矩形條,利用Txline大致計算這種結構下應該設置多大的GSG間隙。
選擇合適的射頻連接器,可以看出端口仿真系數就沒有問題了!
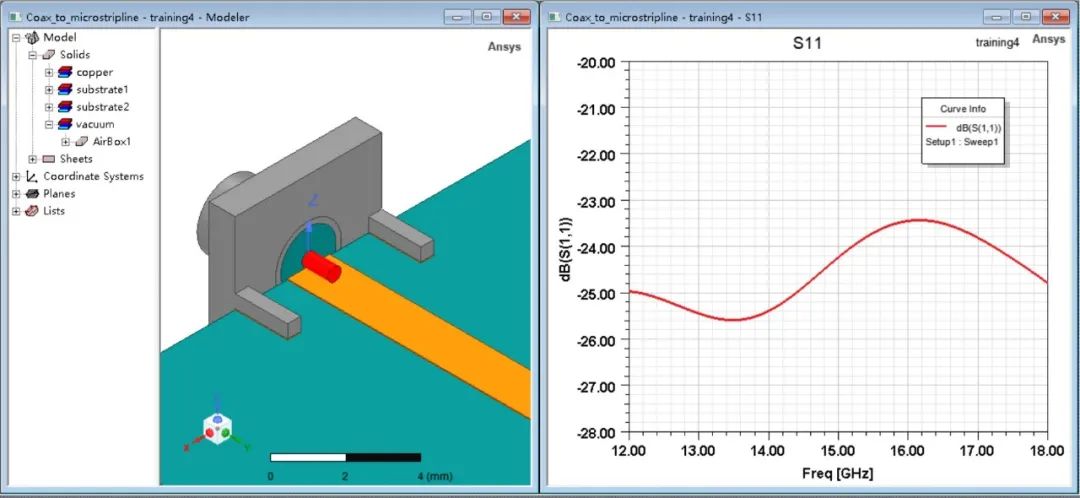
如果連接器種類已經沒辦法更改了,還有什么其他方法來緩解這個現象么?
①可以嘗試手動將法蘭盤上金屬柱的長度剪短一點。
②同樣用Txline,重新選擇合適的線寬和間隙,使得計算的共面波導傳輸線的特性阻抗大致為50歐姆,實現50歐姆同軸線-50歐姆共面波導傳輸線-50歐姆微帶傳輸線的三線轉換。
看到這里,是不是就學會了萬無一失了呢?NO!注意你待測試線纜的接口類型,內螺紋還是外螺紋,公頭還是母頭。連接器的接口需要與之相適配。

如果買錯了怎么辦呢?那只有買個轉換器了。如果你轉換器還是買錯了怎么辦?那就只能涼拌咯 !
!
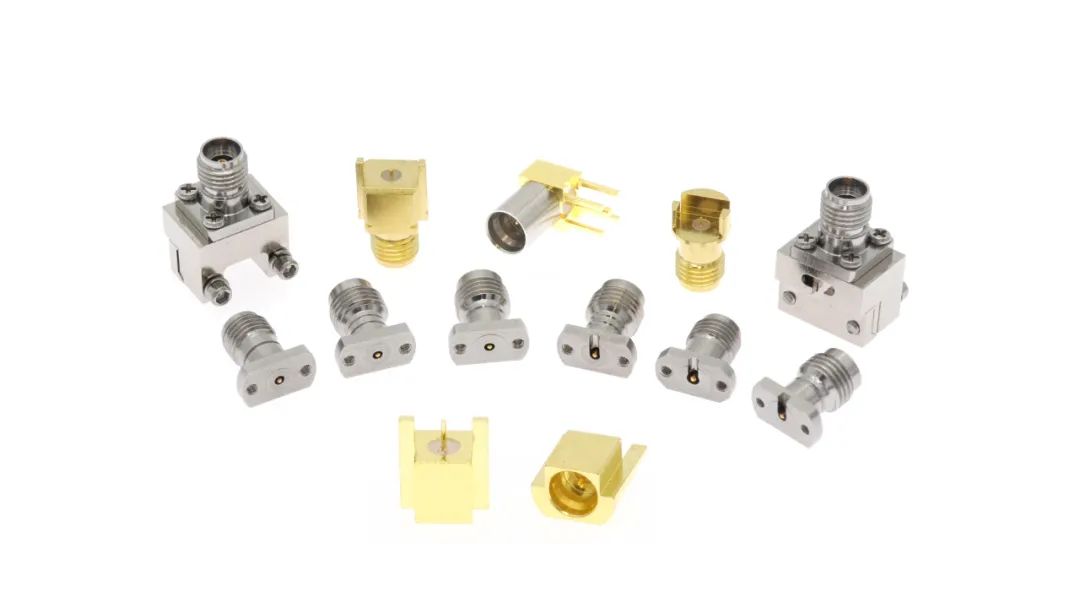 PCB連接器
PCB連接器
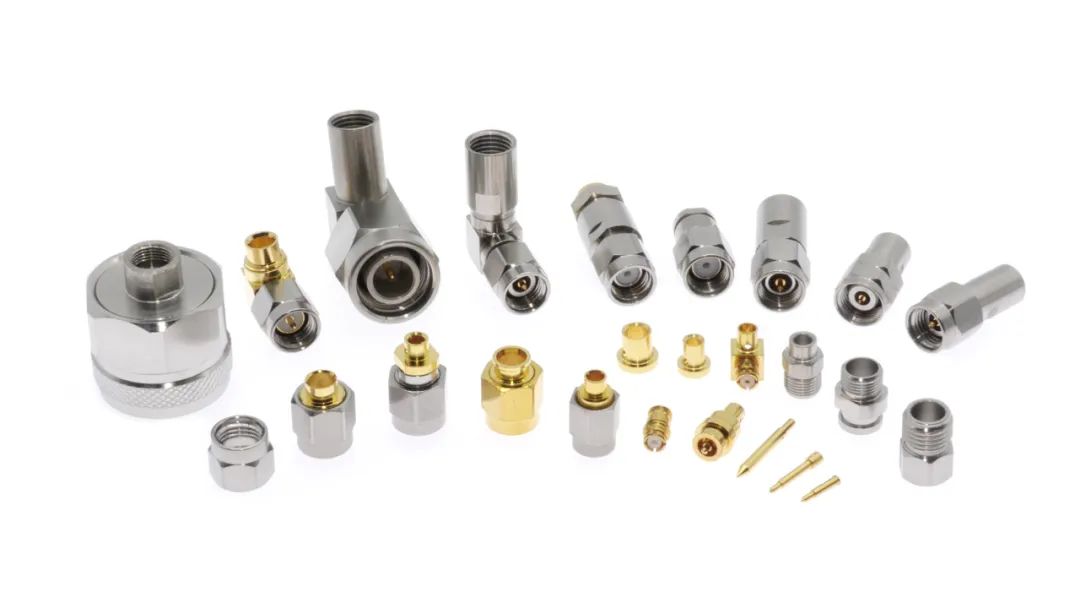 電纜連接器
電纜連接器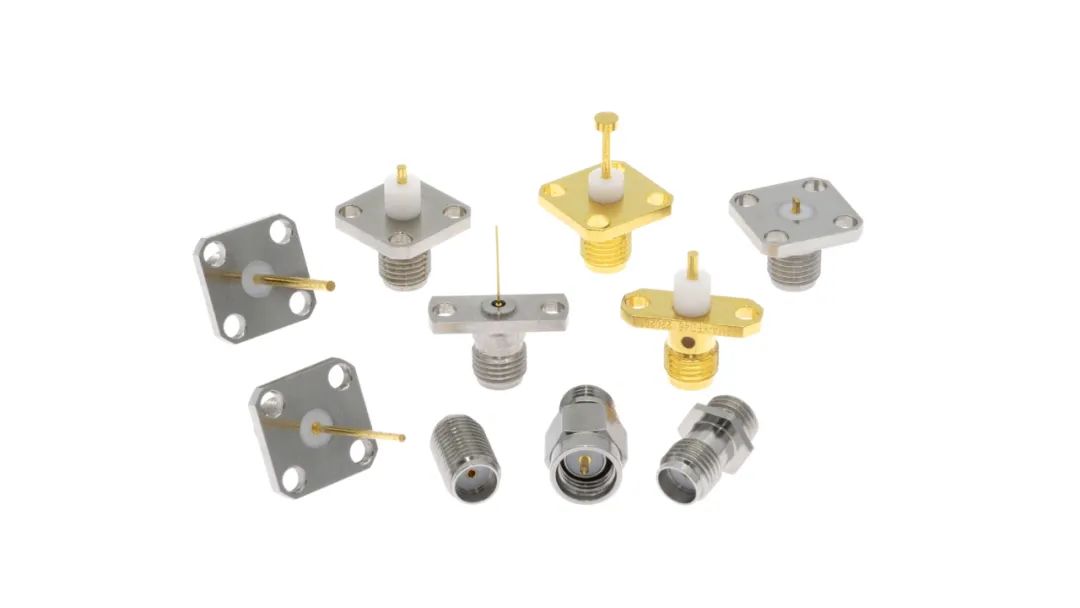
面板式連接器
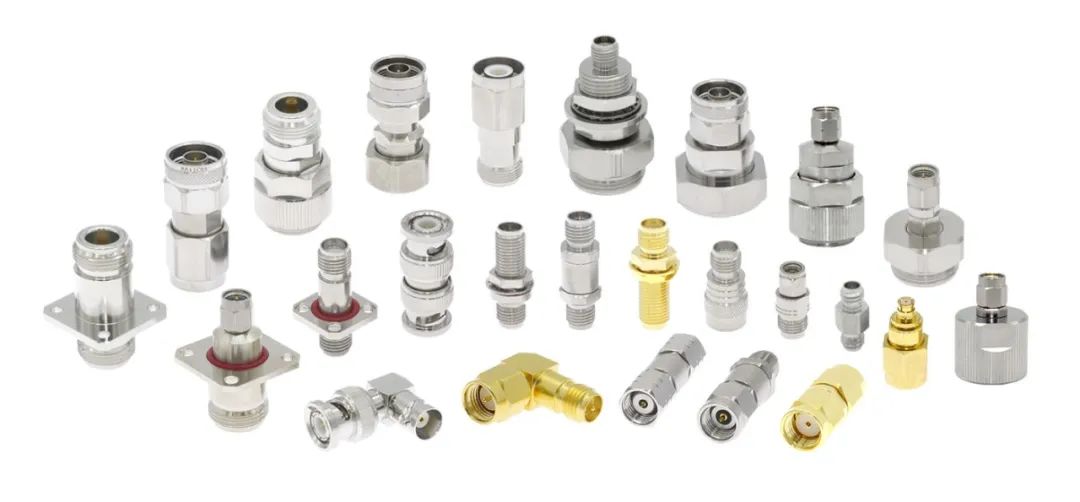

射頻轉接器
What is an RF coaxial connector?
When learning microstrip patch antenna simulation at the beginning, we often use simple wave ports or lumped ports for excitation. However, when the physical processing test, it is necessary to add an RF coaxial connector. Its main function is to realize the interconnection between devices/modules and effectively transmit radio frequency and microwave signals. The RF coaxial connector is usually composed of an inner conductor, an outer conductor, an insulator, and a connecting structure.
Inner conductor: usually a metal needle or metal tube, responsible for transmitting radio frequency signals.
External conductor: Usually a metal sleeve, together with the inner conductor to form a transmission channel, while playing a shielding role to reduce the impact of external interference on the signal. Common outer conductors are stainless steel and copper gold plating, and the connectors of stainless steel outer conductors are usually more durable and have higher manufacturing costs.
Insulator medium: located between the inner conductor and the outer conductor, plays the role of electrical insulation to prevent short circuit between the inner conductor and the outer conductor. Common filling media are PTFE and air media, etc. In order to make the connector have a higher cutoff frequency, some cases will also be filled with air with lower dielectric constant and insertion loss.
Connection structure: used to realize the connection between the connector and other devices, usually including threaded connection, bayonet connection and so on. For example, flanges are mainly used to securely install RF connectors on equipment panels or other structures. Through bolts, nuts and other fasteners, the flange can be tightly attached to the mounting surface to ensure that the connector will not loosen or fall off during use. In addition, in some applications, flanges can also provide a sealing function to prevent external environmental factors such as dust and moisture from entering the interior of the connector, thereby protecting the connector and the connected device.

Classification of coaxial connectors?
Common types of RF coaxial connectors are::
SMA(SubMiniature version A) connector: a widely used small RF coaxial connector, with small size, wide frequency band, stable performance and other characteristics, the general upper limit of the operating frequency of 18GHz, now some manufacturers have been able to SMA maximum frequency to 26.5GHz.

SMA interface diagram
SubMiniature Push-On (SMP) connector: An ultra-miniature push-in RF coaxial connector. The SMP connector is very small in size, which helps to achieve miniaturization and high-density integration of devices, and is suitable for space-limited application scenarios. They typically operate in a wide frequency range, DC up to 40GHz, and even higher for some models.![]()

SMP connector
N-type connector: N-type connector is a common RF connector, its plug and socket have sealing performance, can withstand high power, high voltage and high frequency application environment. N-type connectors feature an internal threaded design and can be used to transmit signals in RF and microwave devices and systems. It is a connector with high versatility, wide frequency range, easy to use and high reliability. N-type connectors usually have 50 ohm and 75 ohm two specifications, the frequency range can be from 0GHZ to 11GHz, and some models can even reach 18GHZ, so N-type connectors are widely used in radar, antenna, satellite communication, microwave measurement and other fields. The advantages of N-type connectors include high mechanical strength, good waterproof and dustproof performance, strong anti-aging performance, stable performance, easy installation and disassembly, excellent contact and signal transmission performance. In addition, the disadvantage of N-type connectors is that they are larger in size and cannot meet the requirements of high-density integration, and the price is slightly more expensive than other types of connectors.
![]()

N-type connector
TNC(Threaded Neill - Concelman) connector: The TNC connector is threaded. The connection is stronger than some bracket connections and can maintain stable connection in vibration and other environments, with good shock resistance. For example, in some mobile communication equipment, TNC connectors can ensure the stable transmission of signals even if the equipment is often subject to vibration.

TNC connector
Bayonet Nut Connector (BNC) : commonly used in video surveillance, instrumentation and other fields. Generally supported signal frequencies range from 0 to 4GHz, with high-precision BNC connectors up to 12GHz or higher. The common characteristic impedance is 50 ohm and 75 ohm, of which 50 ohm BNC connector is mainly used for most RF applications such as RF signal transmission; The 75 ohm BNC connector is commonly used in structures such as broadcast, audio/video, and low-frequency communications.

BNC adapter
In addition, in RF coaxial connectors, sometimes there are 2.4mm/3.5mm/2.92mm connectors. They usually
refer to the size specifications or interface types of connectors, representing different connector characteristicsand application scenarios.
2.4mm connector: has a very high frequency range and can support up to 50GHz and beyond. It is relatively
small in size and has the advantages of low reflection and low loss. It is mainly used in extremely high frequency
RF systems, such as high-end test equipment, millimeter wave communication and other fields.
2.92mm connector:High frequency range and low loss characteristics. It can operate at frequencies as high as40GHz and beyond.
It is often used in high-frequency test and measurement equipment, microwave communication
system, radar and other fields with high frequency requirements.
3.5mm connectorIts frequency range can usually reach about 26.5GHz, up to 34GHz. It is slightly larger than the
2.92mm connector. It is more common in some medium and high frequency RF applications, such as
communication equipment and electronic test instruments.

How to choose a connector?
For our RF and antenna designs, common RF connectors are concentrated in the SMA and SMP types. We choose the corresponding connector category according to the frequency band we need. However, in practical applications, there are small category subdivisions after the selection of large categories. Here it is necessary to adapt to local conditions according to the assembly method of physical design.
For example, side-fed and back-fed microstrip patch antennas can be selected from the two SMA connectors shown below.
 Although these connectors are designed according to the 50 ohm standard, it is easy to cause port mismatch if electromagnetic simulation is not carried out in the actual feed. Take 50 ohm coaxial line and microstrip line cascade as an example. The simulation model shown in the following figure only considers the ideal coaxial line and microstrip line cascade, and the port reflection coefficient of the coaxial line is less than -20dB in 12~18GHz.
Although these connectors are designed according to the 50 ohm standard, it is easy to cause port mismatch if electromagnetic simulation is not carried out in the actual feed. Take 50 ohm coaxial line and microstrip line cascade as an example. The simulation model shown in the following figure only considers the ideal coaxial line and microstrip line cascade, and the port reflection coefficient of the coaxial line is less than -20dB in 12~18GHz.
If you buy an RF coaxial connector directly after the simulation and test it, we will find that the port reflection coefficient will deteriorate rapidly at high frequencies. This is because there are two more metal columns on the flange of the connector, resulting in a mismatch of impedance.

In order to optimize the transmission coefficient, we can consider adding two grounded rectangular bars under the metal column, and use Txline to roughly calculate how much GSG gap should be set under this structure.

Choose the right RF connector, you can see that the port simulation coefficient is no problem!

If the connector type can not be changed, what other ways to alleviate this phenomenon?
①You can try manually cutting the length of the metal column on the flange.
②With the same Txline, suitable line width and gap are re-selected, so that the characteristic impedance of the calculated coplanar waveguide transmission line is roughly 50 ohm, and the three-wire conversion of 50 ohm coplanar waveguide transmission line to 50 ohm microstrip transmission line is realized.
See here, did you learn to be foolproof? Noooo! Note the connector type of the cable you are testing, internal or external threads, male or female. The interface of the connector needs to be adapted to it.

What if I buy the wrong one? Then we'll have to buy a converter. What if you still bought the wrong converter? Then it can only be cold salad pictures !
!
 PCB connector
PCB connector
 Cable connector
Cable connector

Panel connector

RF adapter
上一篇:端子壓接標準及剖面要求 下一篇:連接器行業分析
Previous: Next:Connector industry analysis